Defend against the unseen. Empower your business with advanced cyber security solutions that ensure compliance, minimize risk, and drive trust in every transaction with Savvycom.
Savvycom’s Cyber Security Consulting Services
Trusted by hundreds of businesses
What Are The Key Cybersecurity Challenges?
By 2025, cybersecurity costs are expected to reach $10.5 trillion per year, with 86% of business leaders anticipating that global geopolitical instability will likely result in a catastrophic cyber event within the next two years, marking a 200% increase in disruption levels from 2017 to 2022.
3 Key Challenges
By 2025, cybersecurity costs will hit $10.5 trillion, with 86% of leaders warning geopolitical instability could trigger a catastrophic cyber event – disruptions have surged 200% since 2017.
Evolving Risks
Ransomware attacks surged 13% in 2023, with increasingly sophisticated attacks targeting remote work and critical infrastructure.
Talent Shortage
A cybersecurity workforce gap of 4 million professionals is straining defenses and increasing reliance on automation.
High Costs
Cybercrime will cost $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, compounded by regulatory compliance expenses.
About Savvycom’s Cyber Security Consulting Services
Discover Savvycom’s Comprehensive Cyber Security Outsourcing Services, providing robust protection and peace of mind for your business through our expertise in Professional and Managed Services.
Professional Service
Penetration Testing
• Assists in assessing the system’s cyber security
• Detects dangerous security vulnerabilities on the system
• Improves system defense
• Minimizes system damage
• Supports system and administration and enhances business reputation
Red Team
• Assesses readiness against real cyber attacks
• Tests effectiveness of security technology, people, and processes
• Identifies and categorizes security risks
• Enhances incident detection and response efficiency
• Addresses risks and minimizes vulnerabilities
• Reduces future security costs
• Detects weaknesses missed by other testing methods
Pentest & Red Team Features
- Includes cyber security experts with thinking and acting like hackers
- Operations are not restricted in the manner, scale, and extent of attacks
- Focuses on the most important goal that customers want to achieve
- Authorized to attack and exploit the system
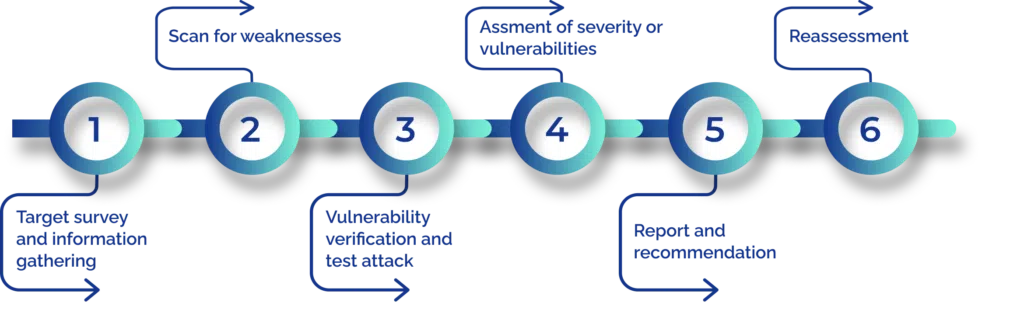
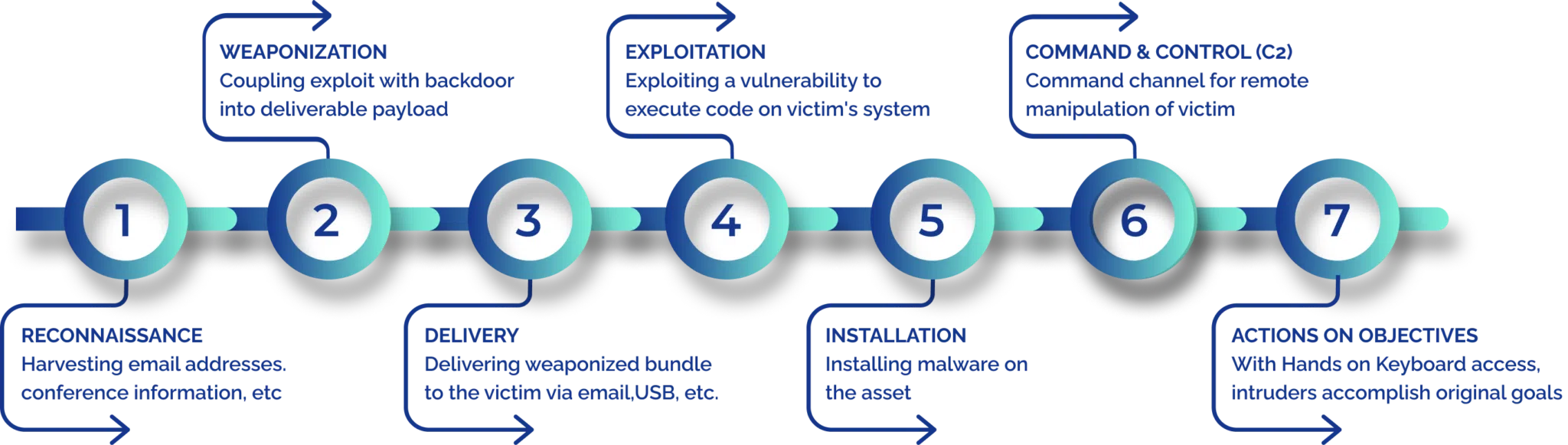
Incident Response & Digital Forensic
Training & Security Drill
Managed Service
1. Security Operation Center (SOC)
A Security Operations Center (SOC) is a centralized facility where a team of IT professionals specializing in information security (infosec) continuously monitors, analyzes, and defends an organization against cyberattacks.
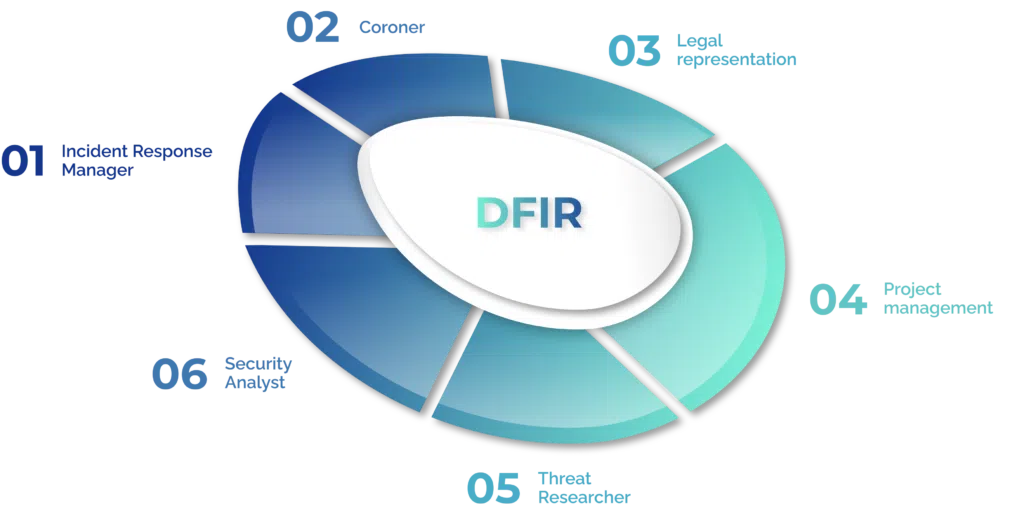
SOC Manager
The leaders of their organization, top-level responsibilities fall to them and they report directly to the CISO.
Compliance Auditor
Plays a key role in the standardization of processes, they ensure protocols and compliance are being followed.
Incident Responder
They rear quickly to alerts and when necessary they react to alerts as soon as possible
SOC Analyst
They are responsible for reviewing past incidents and determining the root cause behind them
Threat Hunter
Run tests across a network to identify weaknesses before they can be exploited
SOCs employ a range of tools for prevention, event logging, automation, detection, investigation, orchestration, and response. SOC teams often have multiple isolated toolsets for different areas of their infrastructure. According to research by analyst firms like Ovum and ESG, most enterprises utilize over 25 distinct tools in their SOCs. These tools may include the following:
• Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
• Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS)
• Network Intrusion Prevention System (NIPS)
• Security Orchestration, Automation and Response (SOAR)
• Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
• Security Analytics Platforms
• Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
• Vulnerability Management Solutions
• Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
• Identity and Access Management (IAM)
• Firewalls
• Log management
2. Network Operation Center (NOC) & Application Managed Service
Our comprehensive framework of managed services addresses the fundamental pillars, enabling any organization to delegate the complete management of its technological environments to our expert services.

Based on your business requirements and maturity level, we will build a customized service by integrating elements from the “Foundation” block with targeted “AddOns”.
- ADD-ONS enhance the “Foundation” block by expanding managed services to include business applications, CLOUD operations, and IT economic and licensing management.
- 360° Management of Business Applications (ERP, CRM, Supply Chain, etc.), covering all functional aspects (Finances, Sales, Purchasing, Manufacturing, Inventory) and related developments.
- Disaster Recovery Services (DRS) and/or High Availability (HA) for your critical environments and applications, customized to your original technologies and aligned with the RTO and RPO parameters your business requires.
- Adapting and maintaining your security parameters and configurations to meet the requirements of the National Security Scheme (ENS), applicable solely to CLOUD environments.
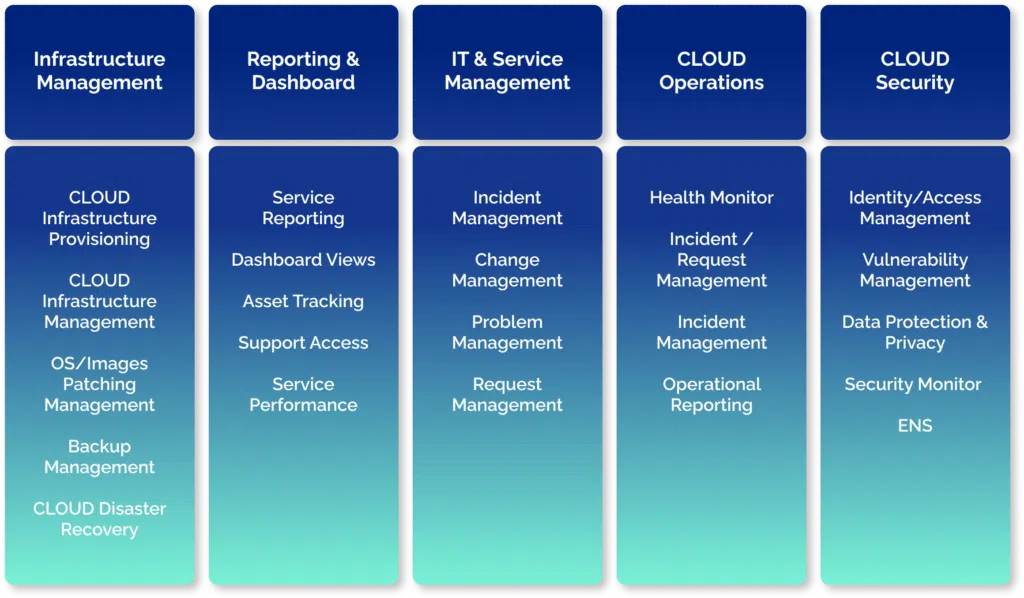
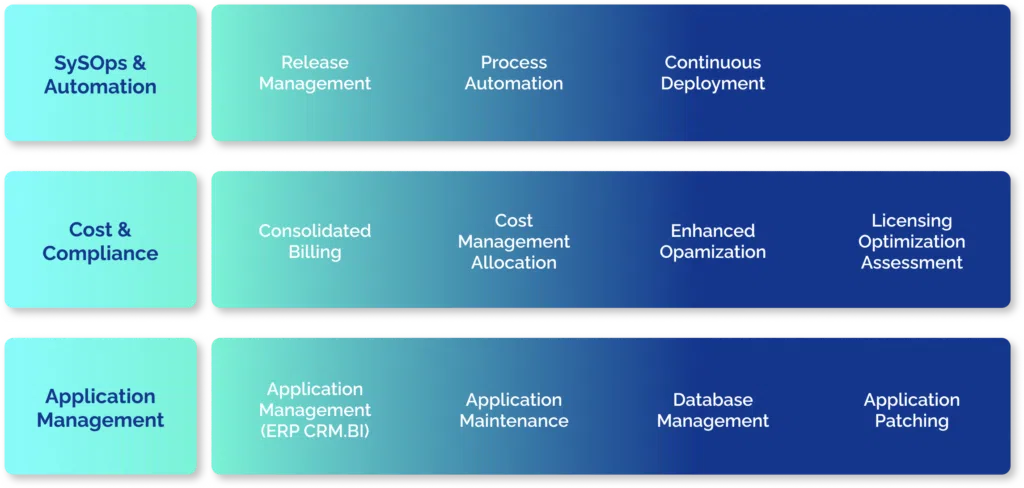
- FOUNDATION services from our managed services model (AMS) provide comprehensive 360° coverage for your IT CLOUD and/or On-Premise environment needs.
- Complete management of your technological infrastructure, including provisioning, administration, and regular patching.
- Backup management based on standards and best practices tailored to the components’ criticality, usage, and characteristics.
- Our specialized Infrastructure & Cloud team dedicated to addressing your requests with strict service control standards.
Industries we excel
Our technical teams’ cross-industry knowledge enables us to integrate best practices and create original solutions from the discovery through to the product’s release stage.

#01 BFSI
Cybersecurity outsourcing enhances threat detection and response, reducing cyber incident response times by up to 70% and ensuring compliance with stringent financial regulations like PCI DSS. It also helps in mitigating financial losses, with an estimated 50% reduction in costs associated with cyber incidents.

#02 Healthcare
Cybersecurity outsourcing strengthens patient data protection, with 80% of healthcare providers seeing improved compliance with HIPAA regulations and a 50% decrease in data breach incidents. Additionally, it enhances patient trust, with 70% reporting increased confidence in the security of their healthcare information.

#03 Government
Outsourcing cybersecurity improves governments’ resilience against cyber attacks, with 60% reporting improved incident response effectiveness and adherence to regulatory requirements like GDPR. This approach also allows for more efficient allocation of resources, with a 40% increase in cybersecurity staff productivity.

#04 E-commerce & Retail
Enhances secure payment processing and customer data protection, with a 45% reduction in cyber incidents and 30% improvement in website security and e-commerce platform protection. This leads to higher customer satisfaction, with a 20% increase in customer loyalty and retention rates.

#05 Energy
Protects critical infrastructure from cyber threats, achieving up to 80% improvement in operational resilience and ensuring compliance with NERC CIP regulations to mitigate risks associated with cyber attacks. Additionally, it facilitates innovation in smart grid technologies, with a 60% increase in secure implementation and adoption of IoT devices.
Why Choose Savvycom As Your Cyber Security Consulting Services Provider
Extensive Expertise
Advanced ransomware and AI-generated attacks, like phishing campaigns, are harder to detect and mitigate.
Advanced Technologies
Stay ahead with continuously updated strategies aligned with the latest advancements in AI and cloud security.
Quality Focus
Deliver resilient, high-assurance security frameworks that prioritize business continuity and data integrity.
Our Talking Numbers
Our Success Stories
Kokkiri partnered with us to create a meditation mobile app that provides relaxing sound recording and psychology classes for healing and relaxation of the mind.
Country: Korea | Industry: Healthcare | Scale: SMEs | Category: Meditation App
30.000+
cross-continent users served at the same time
50.000+
app installs after only 10 days of launching
No.1
app for Fitness and Healthcare

The Cambodian bank offers comprehensive financial services, including loans, bill payments, and banking services, tailored to meet the diverse needs and preferences of their clients.
Country: Cambodia
Scale: 92 branch offices, 10,000+ employees
Industry: BFSI
Category: Financial Mobile App, Data Migration, Integration, Security

SkyThanks is designed to assist user in capturing special moments, lifelong memories and wishes lists, and secure communications and traditional values, so that love lives on.
Country: Australia
Scale: SMEs
Industry: Entertainment
Category: Mobile Diary Apps

Jio collaborated with Savvycom to create a cost-effective, smart engagement system that helps improve community health and bridges the gap in accessing private healthcare between patients and doctors.
Country: Vietnam
Scale: 4 facilities, 200+ doctors
Industry: Healthcare
Category: Telemedicine App

Techstacks We’re Using
Frequently Asked Questions
Do you have more questions? We have answers.
Implementing strong passwords and multi-factor authentication, regularly updating and patching software, conducting employee training on phishing and social engineering, and deploying firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems are crucial steps to prevent cyber attacks.
With our ultimate cyber security consulting services, Savvycom can help your business improve its cybersecurity posture by conducting thorough assessments to identify vulnerabilities, implementing advanced security measures, providing continuous monitoring and incident response, and offering ongoing training and support to ensure your organization stays ahead of evolving threats.



