Boasting a team of over 700 skilled engineers, Savvycom delivers all-encompassing Healthcare IT Solutions, expertly tackling challenges like data security, regulatory compliance, and system integration to ensure utmost comfort and efficiency for healthcare professionals and patient
Healthcare IT Solutions

Best healthcare software development company meet all your digital healthcare needs
From IT planning to healthcare app development, modernization, and maintenance, Savvycom provides comprehensive one-stop solutions for healthcare providers.
Medical IT Solutions
Elevate healthcare delivery with our advanced Medical IT Solutions. Cutting-edge technology is integrated, ensuring seamless patient data management, secure information exchange, and streamlined clinical workflows, transforming patient care into a digitalized, efficient experience.
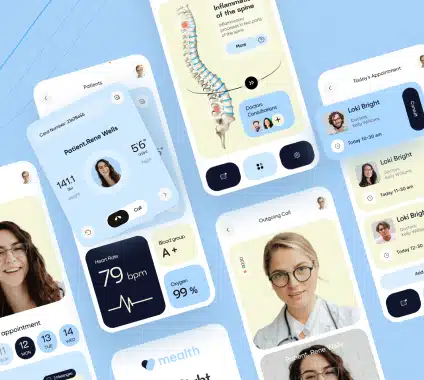

Revolutionize patient care with our specialized Healthcare IT Software. Designed for interoperability and compliance, our software offers robust data security, user-friendly interfaces, and real-time analytics, enhancing decision-making and operational efficiency in healthcare settings.
Digital Healthcare Solutions
Digital Healthcare Solutions now include IoT and Wearable Medical Apps for real-time monitoring, AI-driven Medical Chatbots, and advanced Speech Recognition. We leverage AI for EHR optimization and Blockchain for secure health records, maintaining HIPAA compliance. These enhancements aim to create a more integrated, patient-focused healthcare ecosystem.
Technologies
Leveraging cutting-edge Software Development Methodologies and IT Outsourcing Models, we are equipped to architect and scale exceptional solutions from the ground up for our strategic partners and clients.
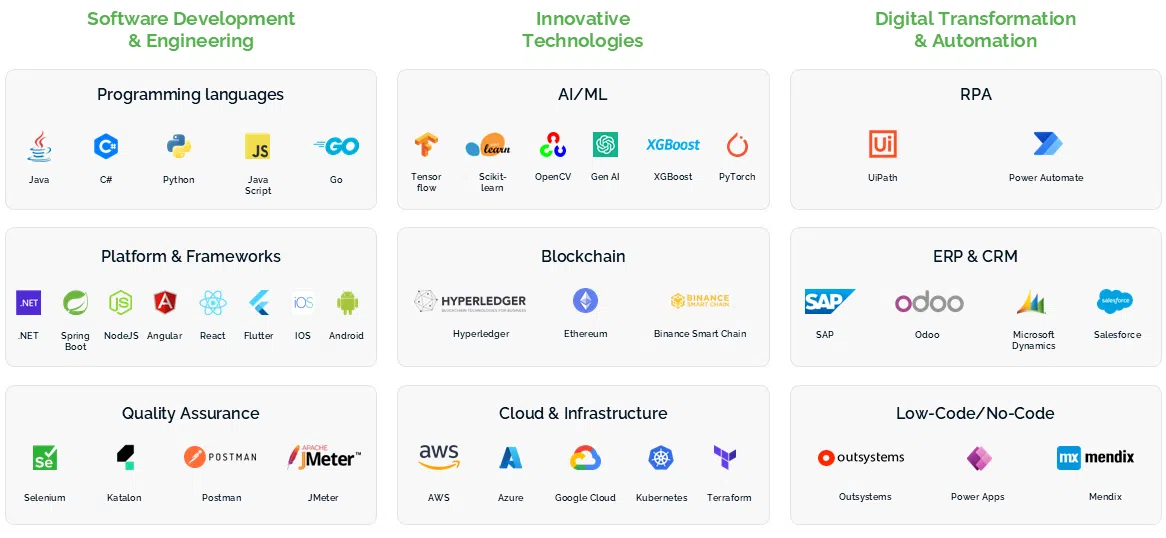
Advanced Technology
Savvycom is dedicated to integrating the latest technological advancements into healthcare, striving to improve the experiences of healthcare providers and patients alike.
AI
- AI-based chronic disease management software
- EHR with AI
- Medical AI chatbots
- Speech recognition
Speech recognition
- Monitoring patients remotely
- Tracking hospital assets
- Comprehensive solutions for monitoring hospitals
- Tracking patients
Blockchain
- Research and trials in clinical settings
- Apps for patients’ personal health records
- Systems for managing and exchanging electronic health records
- Management of medical claims
Computer Vision
- CT
- SPECT
- PET
- MRI
- X-ray imaging, including mammography
- Images from ultrasound
- Various other imaging modalities
Enhance patient care with innovative healthcare software development services
Why Choose Us
Our expertise in improving enterprise healthcare systems goes beyond simple software creation. More than just suppliers, we thoroughly engage with the business side, contributing substantial value to our clients by optimizing and enhancing their operational efficiency and effectiveness.
In-Depth Healthcare Know-How
With profound expertise and experience working with healthcare enterprises, we provide solutions that are perfectly aligned with the evolving needs of the healthcare industry.
Expertise in Local Healthcare Compliance
Understanding the critical importance of compliance in healthcare, our IT solutions was ensured to adhere to local healthcare regulations and standards, maintaining patient safety and data security.
Focus on Medical Examination and Treatment
Specialize in healthcare IT, we enable medical professionals and institutions to concentrate on patient care and medical innovation, while we expertly manage the technological aspects.
Automate Daily Tasks and Staff Management
Our solutions revolutionize healthcare operations, automating patient record management, appointment scheduling, and staff allocation, significantly enhancing clinical efficiency and care delivery.
Clients we worked with
Savvycom takes pride in unwavering commitment to every project we undertake. As a Leading IT Outsourcing Company in Vietnam with a strong engineering focus, we skillfully understand the distinctive needs of diverse clients.
Startups Specializing in Digital Healthcare
Crafting MVPs for healthcare startups, providing a streamlined path to validate your innovative healthcare ideas, attract funding more easily.
Established Software Product Companies
Elevates software products, integrating advanced technologies to enhance functionality and market impact.
Healthcare Services Providers
Streamline administrative and operational processes, enabling Healthcare Provider to focus more on providing exceptional patient care.
Pharmaceutical Companies
Optimize clinical trials, manage regulatory compliance, and foster data-driven research, allowing companies to focus on developing medications.
Governmental and Non-Governmental Healthcare Organizations
Robust healthcare IT strategies for governmental and NGO sectors, focusing on scalable solutions for public health initiatives and community outreach programs.
What Business Leaders Say About Savvycom
We deeply appreciate all feedbacks to improve the quality of our services!



