How Is Blockchain in Banking Transforming the Industry?
The financial industry, particularly banking, is experiencing a paradigm shift with the integration of blockchain technology. According to market.us, the Global Blockchain Technology In BFSI Market size is expected to be worth around USD 218.3 Billion By 2033, from USD 5.5 Billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 44.5% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033. As a software development company, financial institutions are adopting blockchain to enhance efficiency, transparency, and security. From automating transactions to revolutionizing cross-border payments, blockchain is no longer just a buzzword but a crucial tool reshaping banking globally. This blog delves into why blockchain in banking is essential, its impactful use cases, real-world applications, and future opportunities. Read to explore blockchain in banking sector!
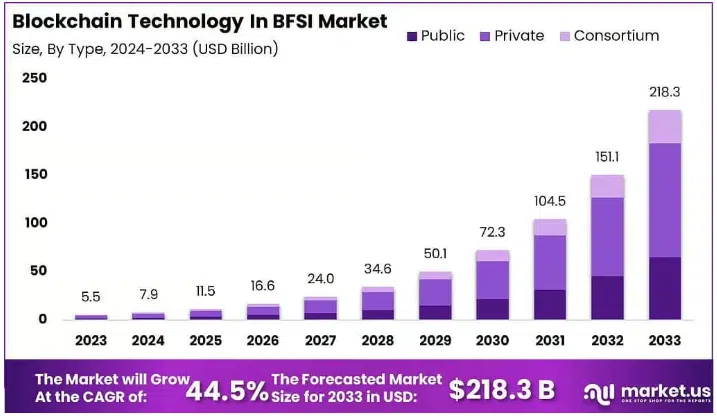
Image source: market.us
Why Is It Essential to Implement Blockchain in Banking?
Blockchain technology is becoming indispensable in the banking sector due to its ability to resolve persistent challenges and meet evolving customer expectations.
- Tackling Inefficiencies: Traditional banking systems rely heavily on intermediaries, resulting in delays and increased transaction costs. Blockchain in banking eliminates intermediaries by offering a decentralized ledger where transactions are recorded directly between parties. For example, clearing and settlement of securities in traditional systems can take up to three days. Blockchain can reduce this process to mere minutes, drastically saving time and operational costs.
- Enhancing Security: Financial institutions face increasing threats from cyberattacks and fraud. Blockchain’s cryptographic nature ensures data immutability, making it nearly impossible for malicious actors to alter records once they are added to the blockchain. According to a study by IBM, over 50% of financial service companies believe blockchain could significantly improve security against data breaches.
- Increasing Transparency: Blockchain in banking provides an auditable trail for all transactions. This transparency fosters trust between banks and their customers while meeting regulatory requirements for real-time reporting.
- Cost Reduction: The Juniper Research estimates that blockchain could save banks up to $27 billion by 2030 in infrastructure, operational costs, and compliance-related processes.
Have a Project Idea in Mind?
Get in touch with Savvycom’s experts for a free consultation. We’ll help you decide on next steps, explain how the development process is organized, and provide you with a free project estimate.
Top Blockchain Use Cases in the Banking Sector
Blockchain in banking a proven disruptor with diverse and transformative applications. Its ability to streamline operations, enhance transparency, and reduce costs has made it a pivotal tool in modernizing financial services. Let’s explore these applications in detail.
Settlement and Clearance Systems
The current settlement and clearance processes in banking are riddled with inefficiencies. Transactions require multiple intermediaries, such as clearinghouses and custodians, leading to delays, higher costs, and error-prone systems. Blockchain technology eliminates these intermediaries by creating a single, shared, immutable ledger accessible to all participants in real-time.
For example, the Depository Trust and Clearing Corporation (DTCC) highlights that using blockchain in banking could potentially save the industry up to $20 billion annually in operational costs by replacing fragmented processes with an integrated digital ledger. Moreover, this transition would reduce settlement times from several days to mere minutes, significantly enhancing cash flow and liquidity for banks.
One practical implementation is by JP Morgan’s Onyx Digital Assets, a blockchain platform designed for intraday repo transactions, allowing instant settlement and optimizing balance sheets for financial institutions.
Cross-Border Payment Transfers
Cross-border payments are notoriously slow and expensive, with traditional methods taking up to five days to process and incurring high fees due to currency conversions and intermediary banks. Blockchain in banking addresses these challenges by enabling secure, near-instantaneous payments at reduced costs.
Ripple, a leading blockchain-based payment platform, has partnered with over 300 financial institutions worldwide, including American Express and Santander. With RippleNet, Santander processes international payments in less than 90 seconds, a stark contrast to the traditional multi-day processing timeline.
Blockchain also reduces transaction costs by up to 70%, especially for remittances. The World Bank notes that such cost reductions could benefit the $700 billion remittance market, primarily aiding low-income households dependent on overseas income.
Fraud Prevention and Security
Fraud and cyberattacks remain persistent challenges for banks, costing the global banking industry over $42 billion in 2022 (PwC). In the past two decades, nearly one-fifth of reported cyber incidents have affected the global financial sector, causing $12 billion in direct losses to financial firms, according to the IMF’s Global Financial Stability Report. Since 2020, direct losses amounted to an estimated $2.5 billion.
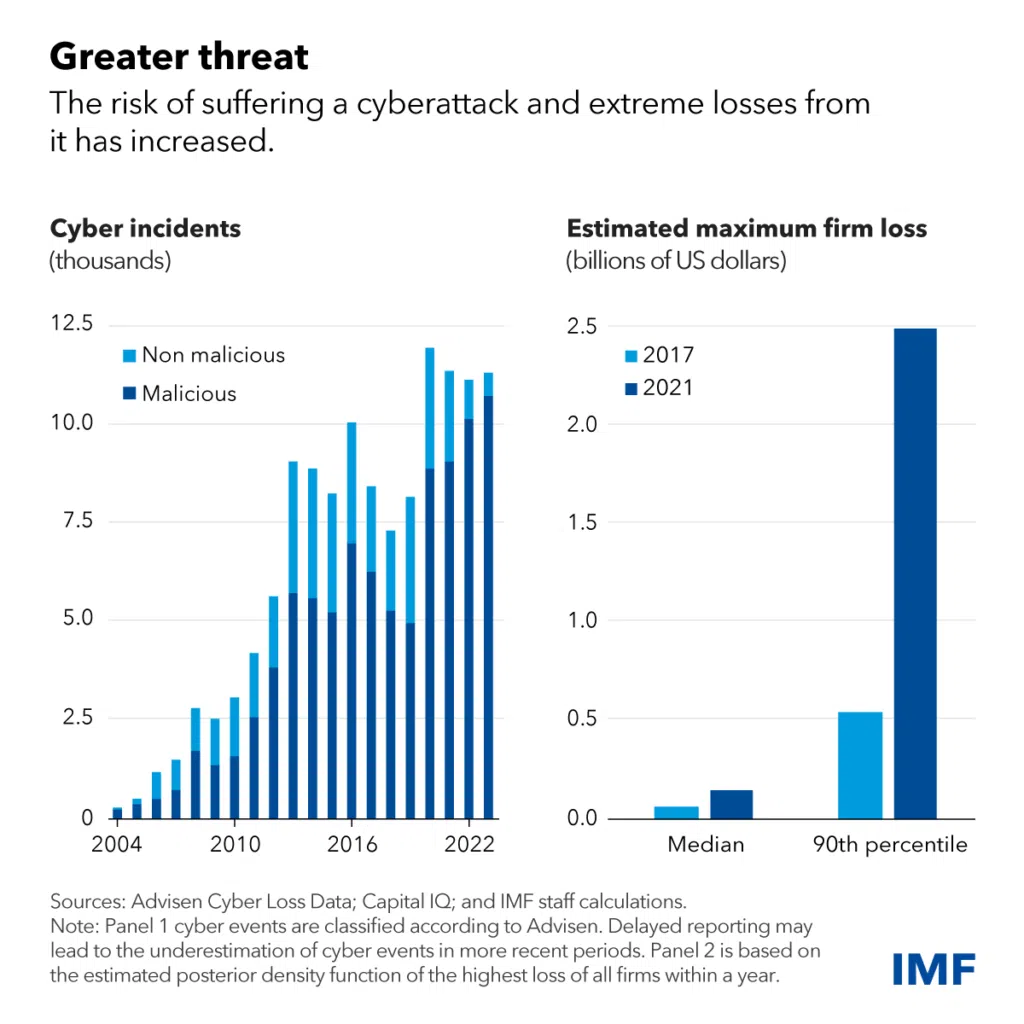
Image source: World Economic Forum
Blockchain’s cryptographic and decentralized design enhances security by ensuring data integrity and providing an immutable record of all transactions. Each transaction on a blockchain is cryptographically secured, verified through consensus mechanisms, and recorded in an immutable ledger, making unauthorized alterations virtually impossible. For instance, Barclays uses blockchain to monitor transaction histories for discrepancies, reducing fraud risks and increasing customer trust.
Blockchain’s potential in fraud detection extends to combating identity theft, card cloning, and insider fraud by providing robust authentication mechanisms.
Asset Tokenization
Blockchain in banking enables the tokenization of physical and digital assets, transforming how assets are owned, traded, and managed. Asset tokenization involves converting real-world assets like real estate, bonds, and commodities into digital tokens stored on a blockchain.
This innovation democratizes investments, allowing fractional ownership and greater liquidity. For example, a real estate property worth $1 million can be tokenized, enabling multiple investors to buy fractional shares. Companies like Harbor and Polymath have developed platforms that tokenize real estate, private equity, and other illiquid assets, making them more accessible to investors globally.
Additionally, tokenization streamlines asset management by automating compliance and reducing administrative overhead.
Loans and Credits
The traditional loan and credit processes are slow, paperwork-intensive, and prone to human error. Blockchain and smart contracts streamline these operations by automating key processes like credit risk assessment, loan disbursement, and repayment tracking.
For instance, Kreditech, a digital bank, leverages blockchain-based smart contracts to enhance the efficiency of its loan processing system. By automating repetitive tasks, Kreditech has improved operational efficiency by 30% and reduced loan approval times significantly.
Blockchain’s transparency also builds trust by ensuring lenders and borrowers can track the loan lifecycle in real-time.
Customer KYC (Know Your Customer)
KYC compliance is critical for banks but comes with substantial costs and inefficiencies. According to a Thomson Reuters survey, financial institutions spend up to $500 million annually on KYC processes.
Blockchain in banking offers a solution through a shared, decentralized KYC system where customer data is verified once and securely stored on the blockchain. Financial institutions can access this data as needed, eliminating redundancy.
For example, India’s Central Bank has explored blockchain for KYC verification to streamline processes across multiple banks, reducing costs and enhancing user experience.
Digital Identity Management
In a digital-first world, securing customer identities has become a top priority for banks. Blockchain technology provides a robust solution for managing digital identities by enabling customers to have greater control over their data.
According to the World Economic Forum, blockchain could prevent identity theft, which caused $5.8 billion in damages globally in 2022. Solutions like Civic use blockchain to allow customers to share identity data only when necessary, reducing exposure to breaches.
This approach strengthens trust while aligning with evolving data privacy regulations like GDPR.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements coded with predefined conditions. Once these conditions are met, the contract executes itself without the need for intermediaries.
In banking, smart contracts automate processes such as loan agreements, insurance claims, and supply chain payments. For example, a mortgage can be processed entirely through a smart contract, ensuring that payments are made directly to the seller once all predefined conditions (e.g., inspections and approvals) are met.
Blockchain-based smart contracts enhance transparency, reduce processing times, and lower operational costs, making them a valuable tool for modern banks.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance is a major cost driver for banks, with global spending on regulatory technology expected to exceed $130 billion by 2025. Blockchain in banking simplifies compliance by providing regulators with real-time access to transparent, tamper-proof records.
The technology automates reporting, audit trails, and anti-money laundering checks, significantly reducing manual efforts and associated costs.
Trade Finance
Trade finance involves extensive documentation and verification, often resulting in delays and disputes. Blockchain in banking digitizes the entire process, offering a single, immutable source of truth accessible to all stakeholders.
For instance, HSBC partnered with IBM to implement blockchain in trade finance, reducing transaction times by over 50% and enhancing operational transparency.
Mortgage and Property Management
Blockchain in banking simplifies the traditionally cumbersome process of property transactions by recording all activities on an immutable ledger. From verifying ownership to automating payments, blockchain creates a seamless experience for buyers, sellers, and banks.
In Dubai, property transactions are fully digitized on a blockchain platform, reducing paperwork, enhancing transparency, and saving millions of dollars annually.
Security and Efficiency
Blockchain in banking inherently enhances system resilience by decentralizing data storage and ensuring transparency. This reduces downtime, minimizes operational errors, and protects against single points of failure.
By addressing key pain points like fraud, inefficiency, and high operational costs, blockchain positions banks to deliver superior services while meeting evolving customer expectations.
Benefits of Blockchain in Banking
The adoption of blockchain in banking offers transformative benefits that address longstanding challenges in the financial sector. By leveraging the decentralized, secure, and transparent nature of blockchain technology, banks can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and provide superior services to their customers. Here are some of the key benefits:

Image source: Appinventiv
- Enhanced Security and Fraud Prevention: Fraud and data breaches are significant concerns for the banking industry. Blockchain’s decentralized and tamper-proof ledger ensures that transaction data is immutable and highly secure. This reduces vulnerabilities to fraud, hacking, and unauthorized access, protecting both banks and their customers.
- Cost Efficiency: Traditional banking processes often involve multiple intermediaries and manual verifications, leading to high operational costs. By adopting blockchain in banking, institutions can automate processes like settlements, KYC, and compliance checks, significantly cutting costs.
- Faster Transactions: Cross-border payments and settlements are notoriously slow, often taking days to complete. Blockchain in banking enables near-instantaneous transactions by eliminating intermediaries. For example, Ripple’s blockchain platform allows international payments to be processed in seconds, transforming how banks handle global money transfers.
- Improved Transparency: Blockchain’s distributed ledger ensures that all transaction records are visible to authorized parties in real time. This transparency builds trust between banks, regulators, and customers by providing a clear, auditable trail of all financial activities.
- Streamlined KYC Processes: Know Your Customer (KYC) compliance is a time-consuming and costly process for banks, with global KYC costs exceeding $500 million annually. Blockchain allows banks to share verified customer data securely, eliminating duplication of efforts and speeding up the onboarding process.
- Access to Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Blockchain opens the door to decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, enabling banks to offer innovative services such as peer-to-peer lending, decentralized exchanges, and automated smart contract-based financial products. This diversifies revenue streams and attracts tech-savvy customers.
- Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management: With its real-time data-sharing capabilities, blockchain in banking simplifies compliance with evolving regulatory requirements. Blockchain ensures data integrity, making it easier for banks to meet stringent reporting standards and mitigate risks associated with non-compliance.
- Asset Tokenization and Investment Accessibility: Blockchain enables the tokenization of assets like real estate, stocks, and commodities, allowing banks to offer fractional ownership to customers. This democratizes investment opportunities, making high-value assets accessible to a broader audience.
By adopting blockchain in banking, financial institutions can not only improve their existing operations but also position themselves as leaders in a rapidly evolving digital economy. This transformative technology offers the tools needed to stay competitive, innovative, and customer-focused.
Looking For a Trusted Tech Partner?
We’ll help you decide on next steps, explain how the development process is organized, and provide you with a free project estimate.
Challenges of Blockchain Adoption in the Banking Ecosystem
Despite the transformative potential of blockchain in banking, its adoption is not without challenges. Banks face significant technological, regulatory, and operational hurdles that must be addressed to realize blockchain’s full benefits.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Many banks operate on decades-old legacy systems that are not designed to support blockchain in banking and its decentralized architecture. Integrating blockchain into these systems often requires extensive overhauls of existing IT infrastructure.
Legacy systems depend on centralized databases and rigid processes, making it difficult to align them with blockchain’s distributed and real-time nature. For example, implementing blockchain may require rebuilding data pipelines, restructuring workflows, and ensuring interoperability with third-party systems like payment gateways or clearinghouses.
Moreover, banks must ensure that new blockchain systems maintain compatibility with older infrastructure during the transition period, adding to the complexity. This transitional phase often takes years and demands significant expertise, testing, and resources.
Regulatory Uncertainty
The global regulatory landscape for blockchain in banking remains fragmented and evolving. Many governments are still debating how to classify and regulate blockchain-based assets, raising concerns for financial institutions.
For instance, questions around anti-money laundering (AML) compliance, data privacy, and taxation remain unresolved in many jurisdictions. Banks are often wary of adopting blockchain fully due to the lack of standardized global frameworks. For example, while some countries like Switzerland and Singapore have embraced blockchain-friendly policies, others maintain restrictive or unclear regulations.
Without clear regulatory guidance, banks risk non-compliance or penalties, making blockchain adoption a complex decision.
Scalability Issues
The scalability of blockchain networks is a critical concern for the banking sector. While blockchain in banking offers unprecedented transparency and security, its efficiency diminishes as transaction volumes increase.
For instance, popular public blockchains like Ethereum face network congestion during high usage periods, leading to slower processing times and increased costs. In a banking environment where thousands of transactions occur every second, such bottlenecks are unacceptable.
Efforts to address scalability—such as Layer 2 solutions, sharding, and consensus mechanism improvements—are still under development. Banks must carefully weigh the benefits of blockchain against its current limitations in handling high transaction volumes.
High Initial Investment
Implementing blockchain in banking requires significant upfront costs, particularly for developing custom solutions tailored to an institution’s specific needs.
Costs include:
- Procuring and maintaining blockchain infrastructure.
- Hiring skilled developers familiar with blockchain protocols.
- Training existing staff to understand and operate blockchain systems.
These expenses can be a major barrier, especially for smaller banks or credit unions with limited budgets. Additionally, the return on investment (ROI) for blockchain projects may not be immediately apparent, making it challenging for banks to justify the initial expenditure to stakeholders.
Key Innovations and Opportunities in 2025
The future of blockchain in banking is highly promising, with innovations poised to reshape the industry by 2025. These advancements address current challenges and unlock new opportunities for growth and efficiency.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
CBDCs represent one of the most significant blockchain-driven innovations. By 2025, more than 80% of central banks are expected to explore or launch blockchain-based digital currencies.
CBDCs use blockchain to provide faster and more secure transaction capabilities, streamline monetary policy implementation, and enhance cross-border payment systems. For instance, China’s digital yuan project, which leverages blockchain, is already being piloted in multiple regions and could serve as a model for other nations.
The adoption of CBDCs will revolutionize the banking industry by reducing reliance on traditional payment systems, enhancing transparency, and lowering transaction costs.
Hybrid Blockchain Models
Hybrid blockchain models combine the strengths of public and private blockchains, offering scalability, security, and privacy tailored to banking needs.
For example, hybrid blockchains enable banks to process sensitive customer data on a private chain while utilizing public chains for transparency and auditability. These models are particularly advantageous for use cases like KYC, trade finance, and regulatory compliance.
The shift toward hybrid blockchains in banking is expected to gain momentum by 2025, driven by their ability to address privacy and scalability concerns effectively.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Integration
Decentralized finance, or DeFi, is another area where blockchain in banking will expand its influence. By eliminating intermediaries, DeFi platforms enable direct access to financial services like lending, borrowing, and trading.
Banks are beginning to explore partnerships with DeFi platforms to offer customers innovative products. For example, collateralized lending via DeFi can provide users with faster and more transparent loan options compared to traditional banks.
By 2025, DeFi integration is expected to evolve further, blurring the lines between traditional banking and decentralized finance. This shift could redefine how financial services are delivered, making them more accessible and efficient.
Elevate Your Blockchain in Banking Journey with Savvycom
Understanding how blockchain works is essential for any banking institution striving to remain competitive in the rapidly evolving financial landscape. Savvycom is proud to be one of the top blockchain app development companies, offering tailored solutions designed to transform financial services and drive innovation in the banking sector.
At Savvycom, we recognize that the potential of blockchain extends far beyond banking. Our team understands the importance of blockchain in various industries, including healthcare, retail, and manufacturing, but we specialize in industries like BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance), where trust, security, and efficiency are paramount.
As a trusted software development company, Savvycom has extensive experience in blockchain, ensuring banks unlock their full potential. Whether you’re exploring new blockchain use cases, scaling existing solutions, or driving digital transformation, Savvycom provides the expertise and support to guide you every step of the way. Partner with us today and harness the full potential of blockchain in banking to elevate your financial services to the next level.
Tech Consulting, End-to-End Product Development, Cloud & DevOps Service! Since 2009, Savvycom has been harnessing digital technologies for the benefit of businesses, mid and large enterprises, and startups across the variety of industries. We can help you to build high-quality software solutions and products as well as deliver a wide range of related professional services.
Savvycom is right where you need. Contact us now for further consultation:
- Phone: +84 24 3202 9222
- Hotline: +1 408 663 8600 (US); +612 8006 1349 (AUS); +84 32 675 2886 (VN)
- Email: [email protected]


