How Blockchain in Education is Transforming Credentialing and Data Security
The education sector has always embraced technological advancements to enhance teaching, learning, and administrative processes. Blockchain technology, known for its decentralization, security, and transparency, has emerged as a transformative force in reshaping education systems. The integration of blockchain in education is revolutionizing traditional methods of storing academic records, verifying credentials, and delivering educational services, paving the way for a more secure, efficient, and equitable learning environment. As a software development company, Savvycom specializing in blockchain technology can help institutions implement these innovative solutions effectively.
In this in-depth exploration, we analyze the significant role of blockchain in education, its key features, benefits, real-world applications, challenges, and its future potential. We also explore the essential components of blockchain that make it so impactful in the education sector, shedding light on how it can address longstanding issues in credentialing, data privacy, accessibility, and more.
What is Blockchain and How Does it Work in Education?
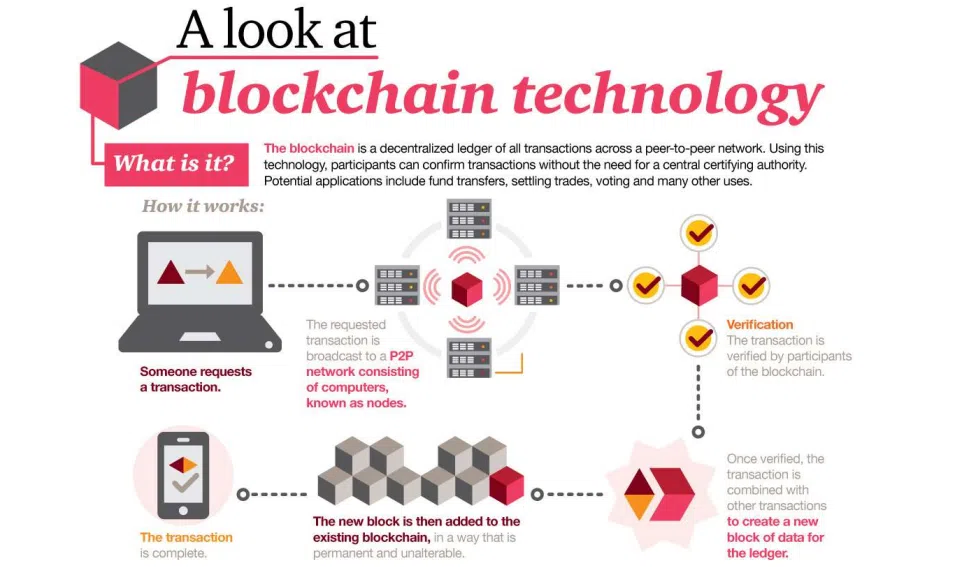
Image source: PwC
Key Features of Blockchain in Education
Blockchain in education offers several transformative features that set it apart from traditional academic systems, making it a powerful tool for managing and securing academic records, credentials, and administrative processes. These key features contribute to the growing adoption of blockchain technologies across educational institutions worldwide.
Immutability
One of the most powerful aspects of blockchain is its immutability, meaning once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or tampered with. This feature ensures the integrity of academic records, making them highly resistant to fraud. For example, if a diploma or transcript is stored on a blockchain, it cannot be changed or falsified without detection, ensuring authenticity and trustworthiness in the credential verification process. A report from PwC reveals that blockchain can reduce fraud in educational credentials by up to 90%, enhancing the credibility of digital certificates and degrees.
Decentralization
Another fundamental advantage of blockchain in education is decentralization. Traditional educational systems often rely on central servers or databases to store sensitive student information, which can be vulnerable to hacking, cyber-attacks, or data breaches. In contrast, blockchain stores data across a distributed network of computers, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access and ensuring greater security for student records. This decentralized nature also removes the reliance on a single point of failure, ensuring that data remains safe and accessible even if certain parts of the network are compromised.
Transparency
Blockchain offers transparency by allowing all stakeholders—students, institutions, employers, and others—to access and verify academic records in a transparent manner. Because blockchain’s ledger is publicly available and verifiable by anyone with the appropriate access rights, it ensures that all actions taken on the system are visible and auditable. This not only builds trust among institutions and students but also makes the entire credential verification process quicker and more efficient.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are another key feature of blockchain in education. These self-executing contracts can automate various administrative functions such as the issuance of certificates, payment processing for tuition fees, or the creation of learning agreements between students and educational institutions. For instance, the University of Nicosia in Cyprus uses blockchain-powered smart contracts to automate tuition fee payments, streamlining the process and reducing human error. By removing the need for manual interventions, smart contracts accelerate administrative workflows, saving time and reducing operational costs.
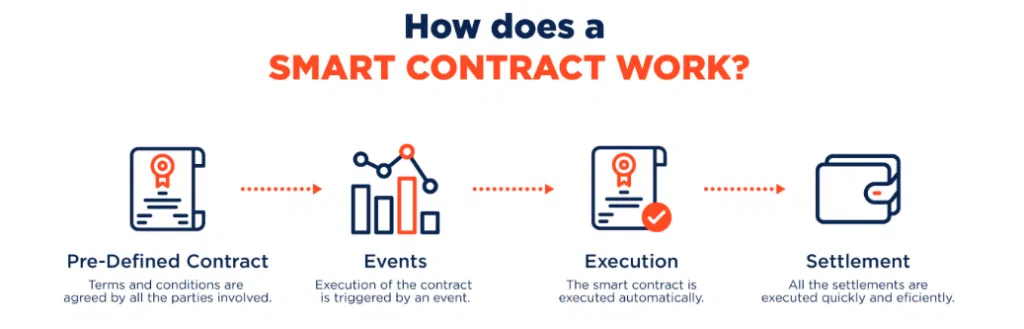
Image source: Blockchain-Based Smart Contracts
Interoperability
Blockchain systems are designed to be compatible with various educational platforms, allowing for seamless data transfer and interoperability between different institutions and countries. This is especially valuable in an increasingly globalized educational environment where students move between institutions or study abroad. Blockchain ensures that students’ academic records, including grades and degrees, are easily accessible and verifiable, regardless of where they studied. This interoperability eliminates delays caused by traditional credential verification processes, making it easier for students to share their qualifications across borders. As blockchain adoption continues to grow, it’s expected that by 2026, the blockchain in education market will reach a valuation of $16 billion, highlighting the significant potential for global integration. These features demonstrate the tremendous potential of blockchain in education to address long-standing issues such as fraud, inefficiency, and limited access to academic credentials. By leveraging blockchain’s security, transparency, and automation, educational institutions can create more efficient, reliable, and secure systems for managing academic records.
Get in touch with Savvycom for a free consultation. We’ll help you decide on next steps, explain how the development process is organized, and provide you with a free project estimate.
Benefits of Blockchain in Education
The integration of blockchain into education has the potential to bring about wide-ranging benefits that address several challenges faced by students, institutions, and other stakeholders in the educational ecosystem. These benefits extend beyond mere credential verification and encompass various aspects of the student experience, administrative efficiency, and global accessibility.
Efficient Credential Verification
One of the most prominent applications of blockchain in education is credential verification. Traditionally, the process of verifying academic credentials is a cumbersome and time-consuming task for employers, institutions, and government bodies. Blockchain offers a solution by providing a secure and tamper-proof record of academic achievements that can be easily accessed and verified. Blockchain enables real-time verification of credentials, minimizing risks of fraud, misrepresentation, and errors. A study shows that blockchain-based credentialing can reduce verification time by up to 80%, enhancing transparency and trust.
For example, universities like MIT and the University of Nicosia use blockchain to issue and verify digital diplomas, streamlining the process. MIT launched a pilot program in 2017 through a partnership with Learning Machine, utilizing the Blockcerts open standard. This initiative allowed over 100 graduates to receive tamper-proof, verifiable digital diplomas stored on the Bitcoin blockchain. The system not only ensured security and transparency but also gave students full ownership of their records, enabling them to share credentials securely with employers or institutions. While the University of Nicosia followed suit by integrating blockchain into its credentialing system, enhancing efficiency and preventing forgery. These advancements demonstrate the transformative potential of blockchain in education by significantly simplifying and securing credential verification processes
Enhanced Data Security and Privacy
One of the critical benefits of blockchain in education is its ability to safeguard sensitive data. With growing concerns over cybersecurity in educational institutions, blockchain offers a decentralized and encrypted approach to data storage, protecting student information such as academic records, personal details, and health data from unauthorized access or tampering. By ensuring that only authorized parties can access the data, blockchain enhances privacy and strengthens trust.
A notable example is the University of Nicosia in Cyprus, which leverages blockchain technology to secure student records and protect them against unauthorized manipulation. This use of blockchain in education not only bolsters data security but also sets a precedent for other institutions to follow.
Global Accessibility and Mobility
The decentralized nature of blockchain in education promotes global accessibility, enabling students to easily share their academic credentials across borders. This capability is crucial in a globalized world where international mobility for education and work is increasingly common. Blockchain simplifies the recognition and verification of qualifications, removing traditional administrative hurdles.
For instance, the European Union’s “Blockchain for Education” initiative explores how blockchain can streamline the recognition of academic credentials internationally, improving accessibility for students pursuing opportunities abroad. This initiative highlights the role of blockchain in education in fostering seamless and efficient cross-border learning experiences.

Image source: JRC Publications Repository
Cost-Effective and Time-Saving
Administrative inefficiencies in education, such as certificate issuance and record management, often lead to high costs and delays. Blockchain in education addresses these challenges by automating processes, eliminating intermediaries, and reducing paperwork. This results in faster, more cost-effective operations for educational institutions.
For example, the University of Sydney utilizes a blockchain-based system to issue certificates, significantly cutting the time and cost traditionally associated with manual certification. This application of blockchain in education demonstrates how technology can optimize administrative functions and resource allocation.
Personalized and Lifelong Learning
Blockchain in education supports the creation of personalized learner profiles that document an individual’s complete learning journey, including formal education, online courses, and skills-based training. By providing a transparent and verifiable record of achievements, blockchain empowers lifelong learners to build comprehensive portfolios.
Platforms like Coursera and edX leverage blockchain technology to issue digital credentials and badges, enabling learners to showcase their achievements in a secure and accessible format. This application of blockchain in education facilitates the recognition of non-traditional learning and enhances employability in a rapidly evolving job market.
Applications of Blockchain in Education
Blockchain in education is transforming how academic institutions manage credentials, administrative processes, intellectual property, and peer-to-peer learning. Here’s how it applies across key areas:
Credentialing and Certification Systems
Blockchain enables institutions to issue tamper-proof digital credentials. These certificates are easily shareable and verifiable, simplifying cross-border recognition. For example, MIT employs blockchain for issuing digital diplomas, ensuring secure access and seamless verification for graduates and employers.
Smart Contracts for Educational Transactions
Smart contracts automate tasks like tuition fee payments and certificate issuance. The University of Nicosia uses blockchain smart contracts for tuition fee management, providing a secure and automated payment process.
Intellectual Property and Research Sharing
Blockchain’s ability to timestamp and secure IP rights is vital for academic research. Researchers can safeguard their contributions, ensuring traceability and originality. Platforms like Ujo Music demonstrate blockchain’s utility in managing IP rights, a model applicable to academic publishing.
Peer-to-Peer Learning Platforms
Decentralized learning platforms powered by blockchain foster collaboration and reward-sharing among learners. This approach enhances community-driven education, encouraging peer engagement and knowledge exchange. Blockchain offers a transparent and trust-enhanced environment for such interactions.
Looking For a Trusted Tech Partner?
We’ll help you decide on next steps, explain how the development process is organized, and provide you with a free project estimate.
Challenges of Blockchain in Education
While blockchain in education offers a promising future, its implementation also presents several challenges that need to be addressed for it to reach its full potential. These challenges range from financial concerns to technical hurdles, but with the right solutions, they can be overcome.
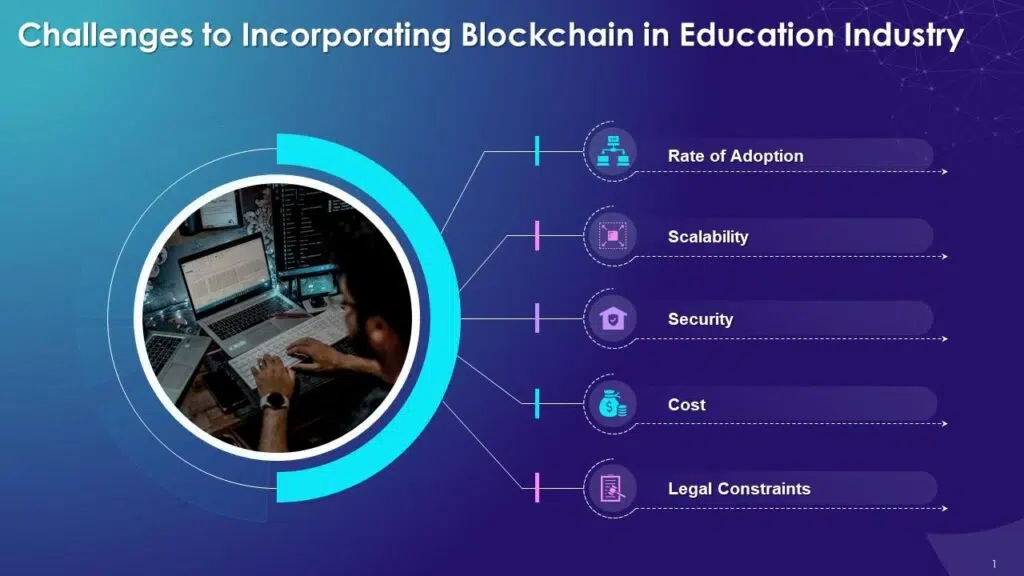
Image source: Slide team
Implementation Costs and Initial Investment
One of the main challenges of adopting blockchain in education is the high initial investment required for its implementation. Setting up blockchain infrastructure, integrating it with existing systems, and training staff can be costly. Smaller educational institutions, in particular, may struggle with the financial burden of integrating blockchain technology, which could result in delays or reluctance to adopt it. According to a report by PwC, while blockchain in education could save institutions money in the long term by reducing fraud and administrative overhead, the upfront costs can be as high as $1.5 million for large universities
Solution: Collaboration between educational institutions and blockchain providers, along with the adoption of open-source blockchain solutions, can significantly reduce implementation costs. Additionally, governments and educational bodies can provide grants or subsidies to support blockchain adoption in schools and universities, making it more accessible.
Interoperability with Legacy Systems
Many educational institutions still rely on traditional, legacy systems to manage student records, grades, and other administrative functions. These systems often operate on outdated technology and are not designed to integrate with newer, decentralized systems like blockchain. The process of integrating blockchain with these legacy systems can be technically complex and costly. A study by the World Economic Forum (WEF) highlighted that while blockchain can be transformative, the lack of compatibility with current technologies remains a significant barrier
Solution: The development of interoperable blockchain platforms that can work alongside traditional systems is crucial to overcoming this barrier. By designing blockchain systems that are compatible with existing educational infrastructure, institutions can implement blockchain gradually without a complete overhaul of their current systems. Blockchain startups and providers are already working on creating hybrid solutions that bridge the gap between legacy systems and blockchain technology.
Regulatory and Legal Issues
Blockchain’s decentralized nature often runs counter to existing legal and regulatory frameworks, which are usually built around centralized systems of data management. In the context of education, the legal recognition of blockchain-based credentials, the protection of student privacy, and the ownership of educational records are all areas that may clash with traditional legal systems. According to the European Union, there is currently no standardized legal framework for blockchain adoption in education, leading to uncertainty for institutions looking to implement it.
Solution: Governments and regulatory bodies must collaborate with educational institutions to establish clear and comprehensive legal guidelines for the use of blockchain in education. These regulations should address concerns such as data privacy, intellectual property rights, and credential verification standards to ensure that blockchain solutions align with existing laws.

Scalability
Scalability remains one of the most significant challenges as the adoption of blockchain in education continues to grow. Blockchain systems need to be able to handle large volumes of data and transactions from thousands or even millions of students, institutions, and employers. As the system scales, ensuring that it remains efficient, secure, and cost-effective becomes increasingly difficult. Blockchain platforms, such as Ethereum, have faced scalability issues due to high transaction fees and slow processing times during periods of heavy use.
Solution: Advances in blockchain technologies, such as Layer 2 solutions (which operate on top of the main blockchain), can help address scalability challenges while maintaining the security and efficiency of blockchain systems. These solutions allow for faster transactions and reduce costs by processing transactions off-chain and only recording essential information on the main blockchain. As these solutions become more widely adopted, they will help educational institutions scale blockchain technology to meet growing demand.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is poised to revolutionize the education sector by solving many of the industry’s long-standing problems related to credentialing, data security, and access to information. The ability to issue, verify, and share credentials in a secure and transparent manner opens new doors for students and institutions alike, leading to improved educational outcomes and better career opportunities.
Educational institutions, technology providers, and governments must work together to overcome the challenges of implementing blockchain in education. However, with the potential to create more equitable and efficient learning environments, the future of blockchain in education is incredibly bright.
Savvycom is right where you need. Contact us now for further consultation:
- Phone: +84 24 3202 9222
- Hotline: +1 408 663 8600 (US); +612 8006 1349 (AUS); +84 32 675 2886 (VN)
- Email: [email protected]


