Software Project Estimation: The First & Foremost Step To Success
Software project estimation approaches assist project managers in effectively estimating critical project parameters such as cost and scope. PMs can then use these estimation strategies to give clients more accurate projections as well as budget the funds and resources they’ll require for a project’s success.
Software project estimation is a critical component of successful software development. By accurately predicting project costs, scope, and so timelines, project managers can effectively allocate resources and manage expectations.
1. What Is Software Project Estimation?

In short, project estimation is a complex process that revolved around predicting the time, cost, and scope that a project requires to be deemed finished. But in terms of software development or software engineering, it also takes the experience of the software outsourcing company, the technique they have to utilize, the process they need to follow in order to finish the project (Software Development Life Cycle). Project Estimation requires the use of complex tools & good mathematical as well as knowledge about planning.
When estimating a software project, consider the following key elements:
- Cost: Determine the financial resources needed to complete the project.
- Time: Estimate the overall project duration and individual task timelines.
- Scope: Define the project’s boundaries and deliverables.
- Risk: Identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies.
- Resources: Assess the required human, technological, and financial resources.
- Quality: Determine the desired level of quality and standards to be met.
2. Which Estimations Take Place During A Project?
Software project estimation is crucial throughout the project lifecycle. In waterfall methodologies, estimates are typically conducted during the initial planning phase. In agile methodologies, estimation may occur at the beginning of each iteration or sprint.
Ultimately, there are six critical elements of a project that benefit from the use of project estimating techniques.
2.1. Cost

While managing software project, cost is one of the three primary constraints. The project will fail if you do not have sufficient funds to complete it. You can help set client expectations and ensure you have enough money to complete the work if you can accurately estimate project costs early on. Estimating software development costs entails determining how much money you’ll need and when you’ll need it.
2.2. Time
Another of the project’s three main constraints is the lack of time. It is critical for project planning to be able to estimate both the overall project duration and the timing of individual tasks.
You can plan for people and resources to be available when you need them if you estimate your project schedule ahead of time. It also enables you to manage client expectations for key deliverables.
2.3. Size or Scope
The third major project constraint is scope. The project scope refers to all of the tasks that must be completed in order to complete the project or deliver a product. You can ensure that you have the right materials and expertise on the project by estimating how much work is involved and exactly what tasks must be completed.
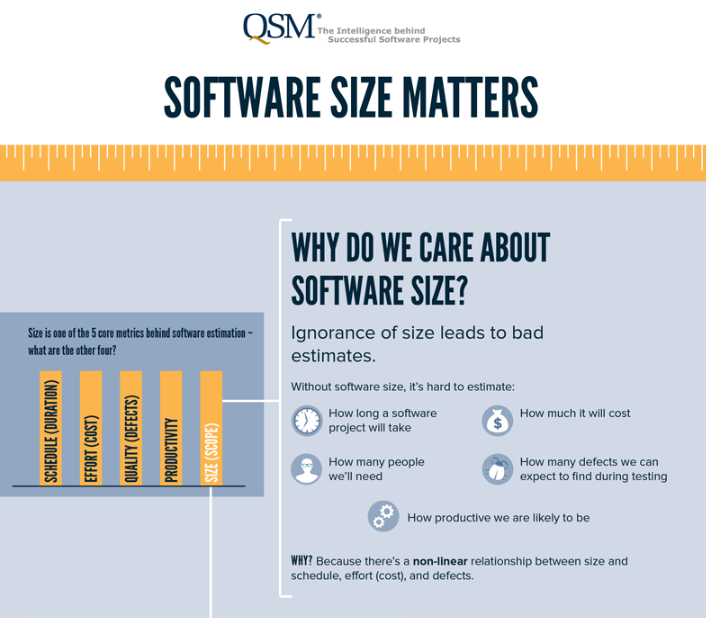
Source: QSM
Three sides of a triangle are often used to describe the three main constraints. This is because any changes to one constraint will inevitably have an effect on the other two. You need to know the scope and schedule to accurately estimate the budget. If one of the three estimates turns out to be higher or lower than you anticipated, the other two are likely to be off as well.
2.4. Risk
Any unforeseen event that could positively or negatively impact your project is referred to as project risk. Estimating risk entails predicting what events will occur during the project’s life cycle and how serious they will be.
You can better plan for potential issues and create risk management plans if you estimate what risks could affect your project and how they will affect it.
2.5. Resources
The assets you’ll need to complete the project are known as project resources. Tools, people, materials, subcontractors, software, and other resources are all examples of resources. Resource management ensures that you have all of the resources you require and make the best use of them.
It’s challenging to plan how you’ll manage resources without knowing what you’ll need and when. This can result in people sitting around doing nothing or materials arriving weeks after you need them.
For Jobs & Vacancies in the USA we recommend checking out Jooble with more than 60 regions USA available for search!
2.6. Quality
Quality is concerned with the completion of project deliverables. Products that must adhere to stringent quality standards, such as environmental regulations, may require more money, time, and other resources than those with lower standards.
Estimating the level of quality required by the customer aids in the planning and estimating the remaining five aspects of your project. Because all six project factors are interconnected, forecasts for one can have an impact on forecasts for the other five.
As a result, applying the same software project estimation techniques to all six areas can help you improve your accuracy.
3. When To Do Project Estimation In Software Engineering?

By definition, estimating is a forecast. And according to a McKinsey report, overruns occur in 66% of all software development projects. This means that most of them fail to meet deadlines, go over budget, and deliver fewer features than expected. There could be various reasons for this, but at Savvycom, we often think that determining a transparent software development process prevents late deliveries and budget overruns.
3.1. Waterfall
While project estimation is essential throughout the project lifecycle, the timing can vary depending on the project methodology. In traditional waterfall methodologies, estimates are typically conducted during the initial planning phase.
3.2. Agile
However, in agile methodologies, estimation may occur at the beginning of each iteration or sprint.
By conducting software project estimation at appropriate stages, you can improve your project’s chances of success and avoid common pitfalls like project overruns.
4. Project Estimation Techniques In Software Engineering?

“Making a workable project estimation that is precise and accurate takes the discipline of a surgeon.” – Savvycom
There is no one-size-fits-all solution, as evidenced by the variety of methods available. Making a perfect forecast that addresses all potential issues is extremely difficult. Software development is a dynamic process in which programmers are constantly learning new technologies and making new discoveries. This has a significant impact on the estimate.
Several techniques can be used for software project estimation, including:
- Top-down estimation
- Bottom-up estimation
- Expert judgment
- Comparative or analogous estimation
- Parametric modeling
- Three-point estimating
4.1. Top-down Estimate
Top-down estimation involves assigning an overall time for the project and then breaking it down into individual phases, work, and tasks based on the work breakdown structure (WBS). This approach is useful when you have a general understanding of the project’s scope and complexity.
If a client specifies that the project must be completed in six months, a top-down approach allows you to take that overall software development timeline and estimate how much time you can commit to each project activity while still meeting the deadline that has been given by the client.
4.2. Bottom-up Estimate
Bottom-up estimation is the polar opposite of a top-down estimate. You begin by estimating each individual task or aspect of the project using this method. Then you add all of the individual estimates together to create the overall project estimate.
This type of estimate is more accurate than the top-down approach because each activity is assessed individually. However, it takes longer to have a completed software estimation and requires more effort from the project manager as well as business analyst.
4.3. Expert Judgment
Expert judgment is one of the most widely used estimation techniques because it is quick and simple. To estimate projects, this method relies on the expertise and intuition of experts.
It’s most useful when you’re planning a standard project that your team has previously completed or has knowledge about. Top-down and bottom-up estimates can both be made using expert judgment.
4.4. Comparative or Analogous Estimation
Comparative or analogous estimation uses data from similar past projects to estimate the current project. This method can be useful when there is a lack of specific data for the current project.
4.5. Parametric Model Estimating
Parametric modeling applies mathematical models to estimate project parameters based on historical data. This technique can be useful for projects with similar characteristics to past projects.
By understanding and applying these software project estimation techniques, project managers can improve the accuracy and reliability of their forecasts, leading to more successful project outcomes.
4.6. Three-point Estimating
Three-point estimating in software project estimation is a technique for generating bottom-up estimates that are sometimes used. You could assign three durations to a task instead of one; it may look like these: optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely. Your actual estimate is calculated by averaging these three numbers.
The PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) method employs three-point estimating, but it uses a weighted average of the three, with the “most likely” guess receiving the most weight.
|
PERT Distribution |
Estimation = (p + 4m + o) / 6
|
| Triangular Distribution |
Estimation = (p + m + o) / 3
|
5. Step by Step to a Successful Software Project Estimation
Like what we’ve mentioned above: estimation’s goal is to predict the amount of money, resources, and time required to complete a project. But there is a lot to consider depending on the estimation case, be it a new project, changing teams for an ongoing project, or just contemplating a new idea for investment.
We have listed below a few tips to help you better visualize your future development plan:
5.1. Define Project Type and Environment
To effectively estimate your software project, it’s crucial to understand the project’s context and methodology.
- Project type: Determine whether the project is waterfall or agile.
- Project environment: Consider factors such as the team’s experience, the complexity of the project, and any external constraints.
5.2. Understanding The Scope Of Work

Clearly define the project’s scope to avoid misunderstandings and ensure that everyone is aligned on the project’s goals and deliverables.
- Identify key features: Determine the essential functionalities and requirements of the project.
- Create a detailed scope document: Document the project’s scope in a clear and concise manner.
- Obtain stakeholder approval: Ensure that all stakeholders agree on the project’s scope.
5.3. Prioritizing Tasks In The Project
Prioritizing tasks within your software project is essential for efficient resource allocation and timely delivery.
- Identify critical tasks: Determine which tasks are essential for project success.
- Assess dependencies: Understand the relationships between tasks and their dependencies.
- Allocate resources accordingly: Assign resources to critical tasks to ensure timely completion.
5.4. Choosing Estimation Techniques
Software project estimation requires careful consideration of various techniques. Select the most appropriate methods based on your project’s specific needs.
- Top-down estimation
- Bottom-up estimation
- Expert judgment
- Comparative or analogous estimation
- Parametric modeling
- Three-point estimating
5.5. Write Down Every Possibilities
During the project estimation process, it is impossible to specify all conceivable assumptions. However, it is preferable to address as many of them as possible in order to prevent any potential for uncertainty. This will help the parties involved in the estimation process to have a better knowledge of each other.
5.6. Revising Your Estimation
Software project estimation is an ongoing process that may require adjustments as the project progresses. Be prepared to revise your estimates based on new information or changes in project scope.
5.7. Use Software Estimation Tools
There are several software solutions used for estimation. While they won’t do the entire work for you, they will make it easier:
- For this, GitLab, Jira, and other Agile task management services can be used. The man-hours spent on each task can be tracked using time tracking software. This will serve as a reminder in the future.
- Redmine‘s cost estimation add-on makes calculations simple. It lets you set an hourly rate for each task and calculates the total.
- EcoSys can keep track of changes and link man-hours to costs. In a comprehensive table, it provides a complete estimate.
- Google Sheets and Microsoft Excel are also popular. They have calculation capabilities and are more user-friendly.
5.8. Special Request From Client
Be prepared to address any special requests or requirements from your client. While it’s important to meet their needs, ensure that these requests are feasible within the project’s scope and budget.
By following these steps and employing effective software project estimation techniques, you can improve the accuracy and reliability of your project forecasts, leading to successful project outcomes.
From Tech Consulting, Mobile App Development Services, Web App Development Services to #1 Vietnam outsourcing software service! Since 2009, Savvycom has been harnessing digital technologies for the benefit of businesses, mid and large enterprises, and startups across the variety of industries. Savvycom dedicated software development team can help you to build high-quality custom software development services and products as well as deliver a wide range of related professional services.
Savvycom is right where you need. Contact us now for further consultation:
- Phone: +84 24 3202 9222
- Hotline: +1 408 663 8600 (US); +612 8006 1349 (AUS); +84 32 675 2886 (VN)
- Email: [email protected]
Why is Software Estimation So Hard?
Until around 2011 or so, most development teams used the Waterfall methodology to plan projects. Waterfall requires all the specifications of a software project to be defined upfront, which is very helpful to the estimation process.
But now, everyone is shifting their attention to Agile (Kanban, Scrum, etc.). Products are shaped through ongoing stakeholder conversations, and what is delivered may not precisely resemble the initial concept. MVPs (Minimum Viable Products) are released quickly, feedback is obtained, and improvements are made iteratively. While Agile has proved its value as a development framework, it has complicated things from a planning perspective.
So the question we need to answer now is: “How can we accurately estimate within a framework that thrives on continuous unplanned change?”
Which are The Difficulties For Both Front- and Back-end Developers?
Front-end Developers:
- They only receive wireframes for the design.
- The designs look easy, but there are no descriptions of animations.
- They get no specifications for different devices and screen sizes.
- The client doesn't actually know what they want until they see it.
- The client assumes that something is easy to achieve if they’ve seen it on another site.
Back-end Developers:
- The task description isn’t detailed enough.
- You’re new to the project, so you’re either missing the big picture or not understanding the overall business logic.
- The project uses 3rd-party services you aren’t familiar with.
- The project uses a technology you aren’t that comfortable with.
- The project’s requirements change as it progresses (holds true for front-end developers as well).